Spaghetti Model Basics

Spaghetti models, also known as spaghetti plots or ensemble forecasts, are a collection of individual model runs that represent the possible outcomes of a future event. They are used to visualize the range of possible outcomes and to assess the uncertainty associated with a forecast.
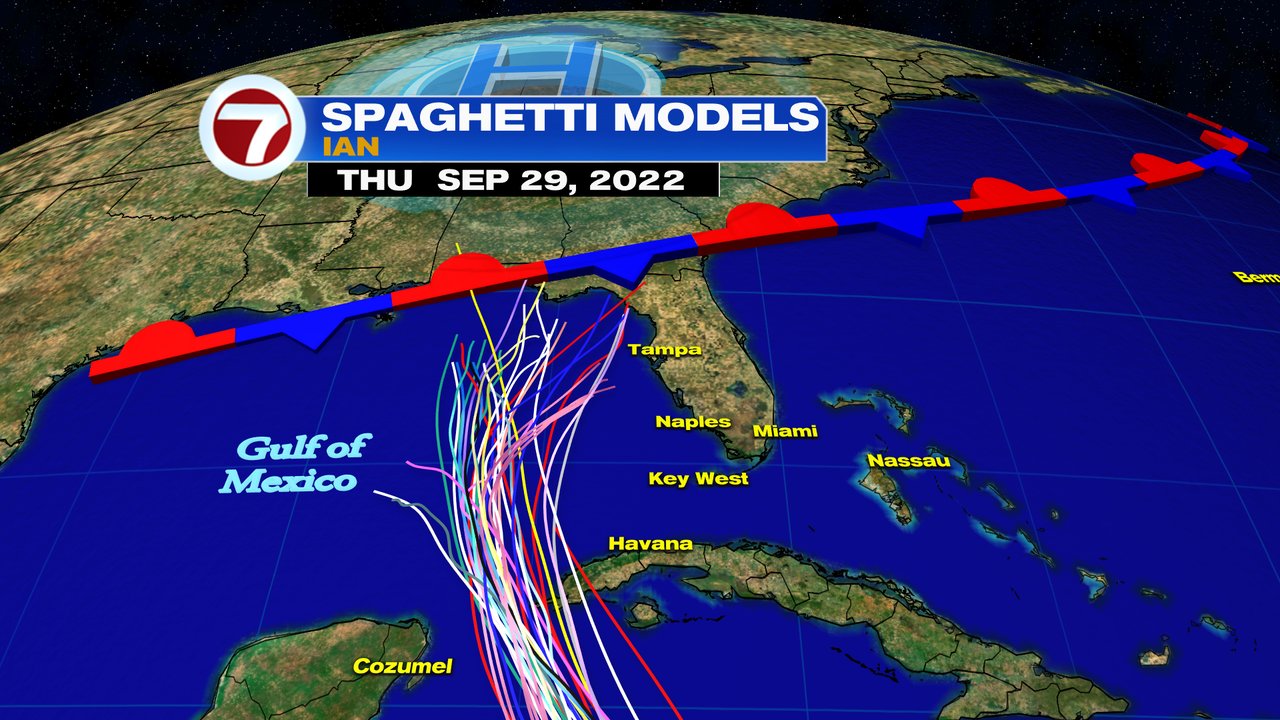
Spaghetti models be like lil squiggly lines that show where hurricanes might go. Dem kinda like a weather guessing game. And check dis out: Barbados Hurricane Beryl was one crazy spaghetti model come true! It make landfall just like it was drawn on dem maps.
Spaghetti models be like a heads up for hurricanes, so we can stay prepared and safe.
The underlying principle of spaghetti models is that each individual model run represents a different possible realization of the future. By running multiple model runs, we can get a sense of the range of possible outcomes and the likelihood of each outcome.
Spaghetti models are simplified representations of complex systems, like weather patterns. Just like how spaghetti can tangle and twist, these models can show how different factors interact. One example is Beryl Puerto Rico , a tropical storm that formed in the Atlantic.
Spaghetti models helped predict its path and intensity, allowing people to prepare and stay safe. By understanding these models, we can better understand the world around us.
Examples of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Weather forecasting: Spaghetti models are used to forecast the weather, and they can provide information about the range of possible temperatures, precipitation, and wind speeds.
- Climate modeling: Spaghetti models are used to simulate future climate conditions, and they can provide information about the range of possible temperatures, precipitation, and sea levels.
- Financial modeling: Spaghetti models are used to forecast financial markets, and they can provide information about the range of possible stock prices, interest rates, and exchange rates.
Spaghetti Model Design and Implementation
![]()
Designing and implementing spaghetti models involve a systematic process that encompasses several key steps. Firstly, it is crucial to define the specific objectives and goals that the model aims to achieve. This provides a clear direction and purpose for the modeling effort.
Once the objectives are established, the next step is to gather and analyze relevant data. This may include historical data, industry trends, and other pertinent information that can inform the model’s structure and parameters. The quality and reliability of the data used are critical to the accuracy and validity of the model.
Challenges and Limitations
Spaghetti models, like any modeling technique, have certain challenges and limitations. One significant challenge lies in the complexity of the models themselves. The interconnected nature of the variables and parameters can make it difficult to understand and interpret the model’s behavior. This complexity also increases the potential for errors and biases in the model’s design and implementation.
Another limitation is the computational cost associated with running spaghetti models. The large number of simulations and iterations required can be computationally intensive, especially for models with a high number of variables and parameters. This can limit the practical applicability of the models, particularly for real-time or time-sensitive decision-making.
Best Practices and Guidelines, Spaghetti models
To ensure the effectiveness and reliability of spaghetti models, it is essential to follow certain best practices and guidelines. One important guideline is to use a structured and modular approach to model design. This involves breaking down the model into smaller, manageable components that can be developed and tested independently. This modularity enhances the model’s transparency and facilitates maintenance and updates.
Another best practice is to validate and calibrate the model thoroughly. This involves comparing the model’s predictions with real-world data and adjusting the model’s parameters to improve its accuracy. Validation and calibration help ensure that the model is reliable and provides meaningful insights.
Additionally, it is important to document the model’s assumptions, limitations, and uncertainties. This documentation provides transparency and allows users to understand the model’s capabilities and potential pitfalls. Clear documentation also facilitates collaboration and knowledge sharing among model developers and users.
Spaghetti Model Applications and Use Cases: Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models have found widespread application in various industries and domains, providing valuable insights and decision-making support.
One key area where spaghetti models excel is risk management. By simulating multiple scenarios and outcomes, these models enable organizations to assess potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. For instance, in the financial sector, spaghetti models are used to evaluate credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, spaghetti models help optimize inventory levels, minimize lead times, and enhance overall efficiency. By simulating different demand patterns and supply chain disruptions, businesses can identify potential bottlenecks and develop contingency plans.
Healthcare
Within the healthcare industry, spaghetti models play a crucial role in disease modeling and forecasting. These models simulate the spread of diseases and help predict future outbreaks. This information enables healthcare professionals to develop effective containment measures and allocate resources accordingly.
Project Management
Spaghetti models also find application in project management. By simulating project schedules and resource allocation, these models assist project managers in identifying potential delays and optimizing resource utilization. This enables teams to complete projects on time and within budget.
Other Applications
Beyond these core applications, spaghetti models have also been used in various other fields, including:
- Energy forecasting
- Transportation planning
- Disaster preparedness
- Cybersecurity risk assessment
Overall, spaghetti models provide a powerful tool for simulating complex systems and assessing potential outcomes. Their versatility and adaptability make them valuable assets in a wide range of industries and domains.